| Attention Before you read this post, I highly recommend you check out my resources page for access to the tools and services I use to not only maintain my system but also fix all my computer errors, by clicking here! |
By following the steps provided in this posted, you should have a much firmer grasps of what virtual memory is and what you should do if receive any virtual memory too low warning messages.
So what is Virtual Memory?
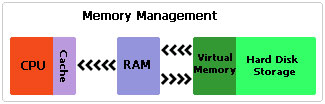
Virtual memory is a Prefetch that exists within the hard drive and memory modules. Before information is taken to the RAM (Random Access Memory), information is first stored in a swap file on your hard drive called Virtual Memory. The size of this swap file can be altered to suit the specifications of your computer. This will ultimately increase the amount of available space that can be used during the execution of applications.
The official name for this area in the hard drive where the RAM image is stored is called Page File. In this area, information from the RAM is stored onto the hard drive and is continuously shared between both the RAM and Page File. The file extension for the page file is .SWP.
The amounts of free space that you have available on your hard drive also plays into the amount of space you can allocate for virtual memory and also initiates those virtual memory too low warning messages.
How Does Virtual Memory Work?
Virtual memory is an integral component of your operating system. Its importance is a direct result of the huge benefits one is able to achieve from using it at relatively low costs to execute.
Continue reading to learn about what virtual memory is; how your computer system actually uses it and how you can configure it to make your system run optimally.
The vast majority of computers have at least 4GB of RAM available for the CPU (Central Processing Unit) to use during the execution of applications. The downside is that this is not nearly enough RAM to have multiple large applications running simultaneously at optimal performance.
For example, a system that has an operating system loaded up, along with various other applications, such as Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Dreamweaver, Microsoft Word and Microsoft Outlook, all running simultaneously with just 4GB of RAM to sustain it, would suffer performance wise. Given that scenario, if the same system had no virtual memory with only the 4GB of available RAM to sustain it, it would almost certainly have to close down an application before it could load up another one.
With the availability of virtual memory however, the system can now allocate segments of an application/program to the swap file that exists on the hard drive. This results in more space being available in the RAM for loading new programs/applications.
This whole process happens in the background, automatically, so you don’t really know it’s happening, though it creates the impression that your system has an overabundance of RAM, despite the fact that it may only have 1GB of RAM, and because it’s considerably cheaper for you to purchase a new hard drive over additional memory modules, focusing on virtual memory and hard drive space, appears more beneficial, from an economic standpoint.
The Drawbacks of Virtual Memory
The speed in which hard drives read and write information is considerably slower to that of RAM; in addition, hard drives are not as efficient at accessing data in small chunks at a time. As a result, if your computer is continuously out of RAM, having to depend almost solely on virtual memory much of the time, then you will notice a considerable drop in system performance. The objective is for you to purchase enough RAM to handle all the programs/applications you intend to run on it, that way, the only time you will notice any real deterioration in performance is when your switching between tasks. It’s in this particular scenario when virtual memory works best.
The opposite of this scenario is when your operating system is made to continuously swap information between the hard drive and RAM. This process is called disk thrashing and seriously affects the speed of the computer.
Virtual Memory Too Low Error Messages
If you are receiving any error messages such as Virtual Memory too low warnings, then there are two viable methods you can use to solve this problem. The first is to purchase additional RAM and the second is to increase the size of your page file so that your computer can run more programs simultaneously. By default, Windows will manage the size of your page file, but it is possible and in most cases necessary for you to change it manually, for smoother running of the OS.
How to Manually Increase Your Virtual Memory
The process you must take to carry out this function varies somewhat depending on the version of Windows you have, however if you’re faced with virtual memory too low warning messages, then you could go about increasing it by doing the following:
1. The first thing you must do is ensure you’ve logged into your computer with administrative rights.
2. Once your computer has finished booting up, click on Start -> Control Panel.
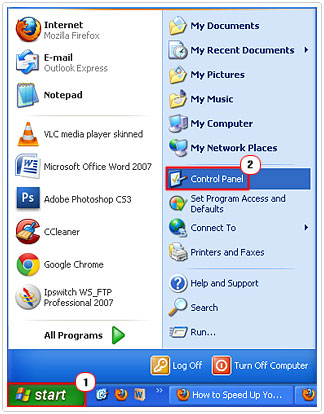
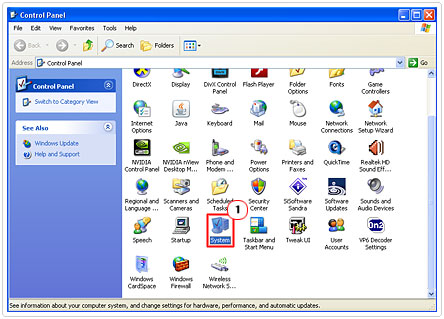
3. Once the Control Panel has loaded up, double click on System.
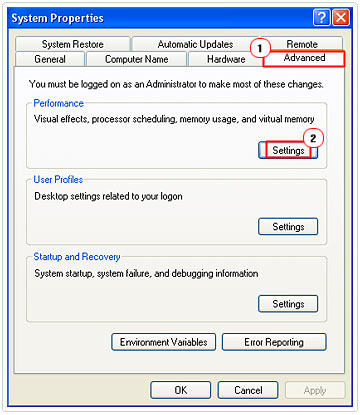
4. This will load up System Properties, from there click on the Advanced Tab, and the Settings button, under Performance.
5. When Performance Options loads up, click on the Advanced Tab followed by Change, under Virtual memory.
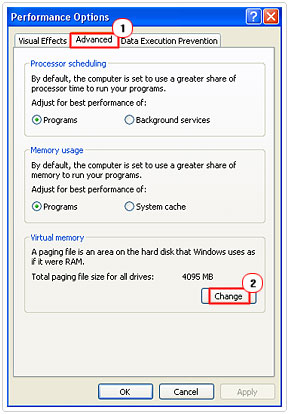
6. Under Drive [Volume Label], select the drive that you would like to alter the Page File on.
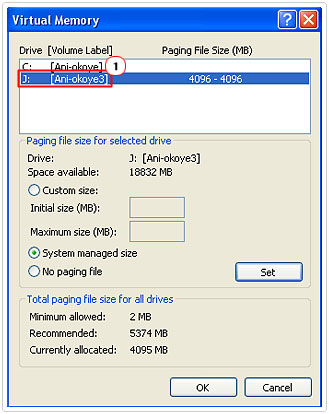
7. Once you’ve done that, click on Custom Size and enter in the Initial size (MB) and Maximum size (MB) of hard drive space you would like to allocate for virtual memory. Once you’ve done that, click on Set then OK.
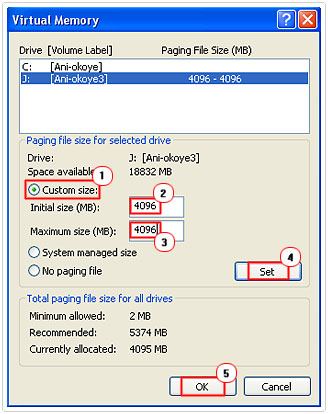
Note: You should be prompted to restart your system, do so by clicking on Yes.
Additional Notes
It’s very important that both your Initial size (MB) and Maximum size (MB) are set to the same amount i.e. 750MB and 750MB. This will ensure your page file doesn’t fluctuate in size.
The value that you set for your virtual memory should be no less than 1.5 times the amount of available RAM on your computer. So if you have 4GB of RAM, then your virtual memory swap file should be 1.5*4GB= 6GB.
Remember, if you have multiple hard drives or partitions, you only need to set your page file for one of these drives, which in most cases is your C:\ Drive.
It’s also very important that you consider the available hard disk space on your computer when setting your page file. Make sure your page file isn’t larger than the available space on your drive and isn’t to small, to avoid virtual memory too low warning messages.
How to Automate the Process
If you’re pressed for time, or currently battling with a virtual memory too low warning issue, then you could adopt a wholly automated process of increasing your virtual memory, by downloading Microsoft Fix it. Simply click on the link below, save the file to your computer and run it.
Microsoft Fix it: http://go.microsoft.com/?linkid=9759543
Additional Notes
This particular tool will automatically change the Initial size (MB) of your virtual memory to 1.5 times that of your RAM and your Maximum size (MB) value to 3 times that of your RAM…providing there’s available hard disk space.
Make sure you run it on the computer that you would like to reconfigure. In addition, you can save the tool to a flash drive or CD and use it on as many systems as you like.
Are you looking for a way to repair all the errors on your computer?

If the answer is Yes, then I highly recommend you check out Advanced System Repair Pro.
Which is the leading registry cleaner program online that is able to cure your system from a number of different ailments such as Windows Installer Errors, Runtime Errors, Malicious Software, Spyware, System Freezing, Active Malware, Blue Screen of Death Errors, Rundll Errors, Slow Erratic Computer Performance, ActiveX Errors and much more. Click here to check it out NOW!


The objective of Virtual Memory systems is the ability to load and execute a process that requires a larger amount of memory than what is available by loading the process in parts and then executing them.
If your virtual memory is low, you’ll need to increase the minimum size of your paging file. Windows sets the initial minimum size of the paging file at the amount of random access memory (RAM) installed on your computer plus 300 megabytes (MB), and the maximum size at 3 times the amount of RAM installed on your computer.
When Windows managed, it becomes variable, meaning you do not have to alter it to reflect hard drive space.